MSSQL Server backup plugin#
This Bacularis plugin enables backing up and restoring Microsoft SQL Server databases.

Core features#
The Bacularis SQL Server backup plugin provides the following functionality:
Logical SQL database backups
Transaction log backups (WAL)
Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR)
Encryption data backups (Service Master Key, Database Master Keys, certificates …)
Backups of remote and local SQL Server instances
Backups of SQL Server instances on Windows
Backups of SQL Server instances on Linux
Restoring databases to the same or a different SQL Server instance
Backup methods#
This plugin supports the following SQL Server database backup methods:
Dump backup method - also known as logical database backup. It creates backups in binary dump format. Two variants are available:
All databases backup - each database is stored in a separate dump file. This method allows restoring selected databases individually.
Selected databases dump - the Bacularis administrator specifies which databases to back up. This method also supports restoring selected individual databases.
Transaction log backup method - backs up the database transaction log.
Encryption data backup method - backs up selected encryption keys (Service Master Key, Database Master Key, certificates, asymmetric keys).
Backup methods can be used independently or combined. For example:
A job can run only the dump backup method.
A job can combine multiple methods, such as dump, transaction log, and encryption data backups.
General requirements#
The SQL Server backup plugin is available in Bacularis version 5.9.0 and later.
To use it, you need:
Bacularis web interface version
5.9.0or later.Bacularis API version
5.9.0or later installed on a Linux host with the Bacula client. The SQL Server instance may be local or remote to the client host.Tools for Microsoft SQL Server (
mssql-tools) installed on the Linux host with the Bacula client (and on the Bacula Director host if separate).Bacula client with the bpipe plugin installed (typically installed by default).
Video guide#
Prepare environment#
Bacula BPIPE plugin#
Check whether the Bacula client used for SQL Server backups has the bpipe
plugin installed. You can verify this using the status client=xxx command
in Bconsole or directly in Bacularis:
*status client=ubuntu-fd
Connecting to Client ubuntu-fd at localhost:9102
ubuntu-fd Version: 13.0.4 (12 February 2024) x86_64-pc-linux-gnu ubuntu 25.04
Daemon started 22-Aug-25 06:34. Jobs: run=81 running=0.
Heap: heap=557,056 smbytes=211,090 max_bytes=1,065,894 bufs=130 max_bufs=196
Sizes: boffset_t=8 size_t=8 debug=0 trace=0 mode=0,0 bwlimit=0kB/s
Crypto: fips=N/A crypto=OpenSSL 3.4.0 22 Oct 2024
Plugin: bpipe-fd.so(2)
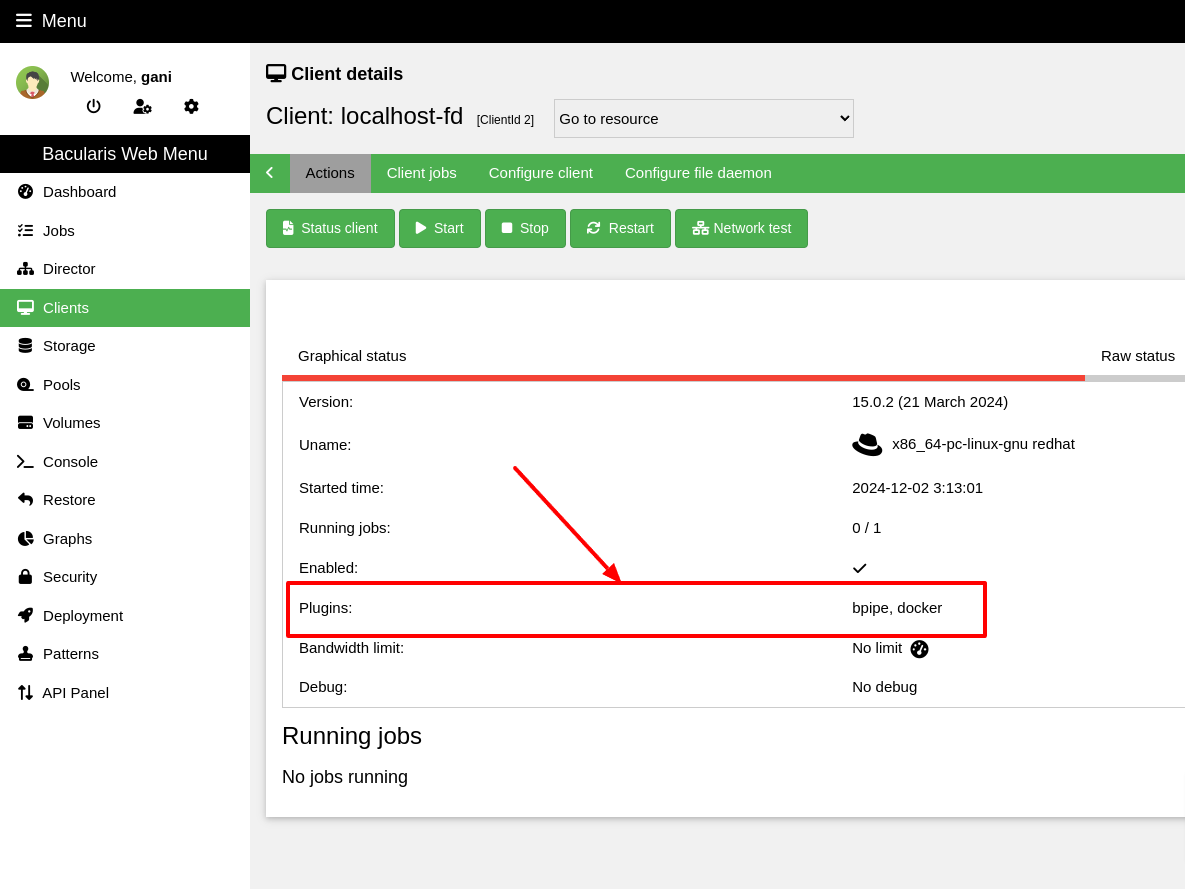
IMPORTANT NOTE: Bacula versions 15.0.0 - 15.0.2 contain a bpipe plugin
bug that causes the Bacula client to crash (segfault) after backups. See how to
solve it: File daemon crashes after running Bacularis plugins (MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MSSQL…).
Bacularis#
The most common setup is to use the Bacularis web interface and Bacularis API from the same installation. However, they may run on separate hosts if needed.
Both components must be in version 5.9.0 or later.
SQL Server Tools#
Install Tools for Microsoft SQL Server (mssql-tools) on the hosts running
Bacula Director and Bacula Client. If both services run on the same host, install
the tools only once.
Installation instructions are available on the Microsoft website:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-setup-tools
Common backup directory#

All SQL Server backup and restore operations are always performed from the Linux host running the Bacula client, regardless of whether SQL Server runs on Windows or Linux. A dedicated shared directory, called the common backup directory, is required to exchange data between Bacularis and SQL Server during backup/restore.
It must be defined twice in the plugin configuration:
As the backup directory on the SQL Server host (e.g.,
C:\BACKUP)As the backup directory on the Bacula client host (e.g.,
/mnt/BACKUP)
Both paths refer to the same location, accessible from:
SQL Server
The Bacula client on Linux
If SQL Server runs on Windows, create a directory on Windows (e.g., C:\BACKUP),
share it, and mount it on the Linux Bacula client (e.g., /mnt/BACKUP).
If SQL Server runs on Linux:
If SQL Server and the Bacula client run on the same host, no network sharing is required.
If they run on different hosts, share the directory using CIFS, NFS or another file-sharing protocol.
Note
Ensure the common backup directory has sufficient space for backup files. The plugin provides an option to delete local copies after backup completion if you wish to save space.
Permissions
Ensure that the system user account running SQL Server has read/write access to the common backup directory. Assign appropriate system user ownership or permissions to that directory.
SQL Server preparation#
Network connection
To allow the plugin to execute remote SQL commands, the SQL Server instance must listen on a network interface and accept connections over TCP/IP. Enable this in SQL Server Configuration Manager:
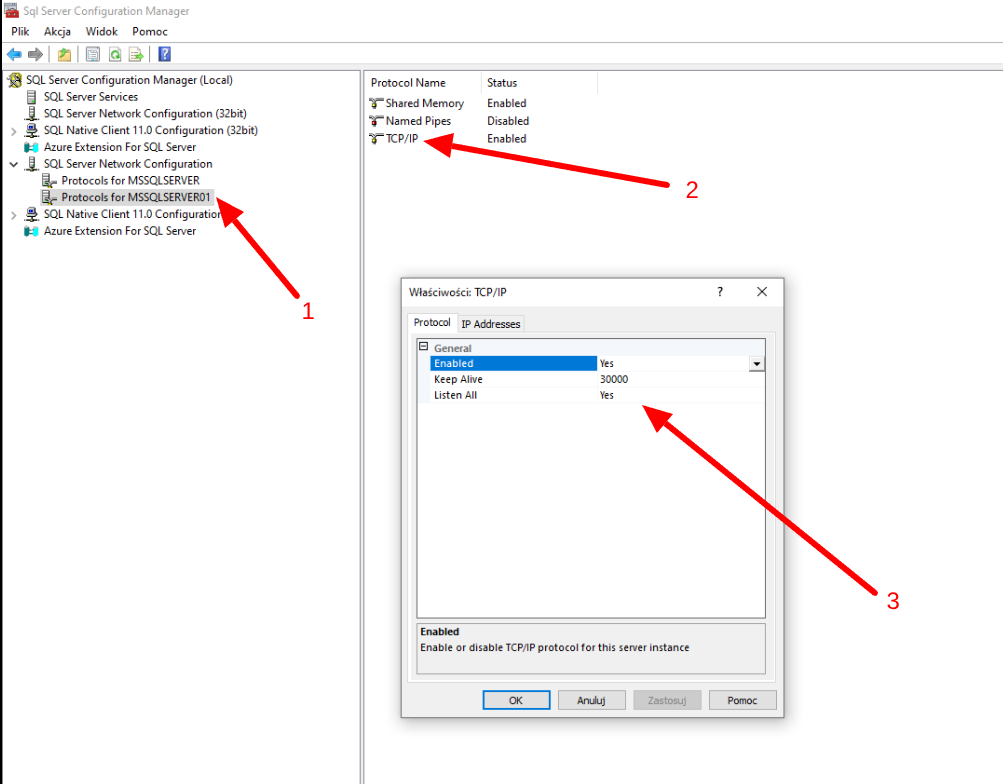
After enabling it, restart the SQL Server service.
Database user
The database user used with this plugin must have the sysadmin role assigned.
Backup#
Before using the SQL Server plugin, you must prepare the plugin command in the FileSet
resource. This consists of:
Creating the SQL Server backup plugin configuration
Using this configuration in the Bacula
FileSetPlugindirective
You can create the plugin configuration either on the Plugins tab of the Add-ons
page or directly within the FileSet configuration by clicking Add plugin.
In the latter case, configuration creation and FileSet insertion happen in one step.
The configuration window appears after selecting Add plugin:
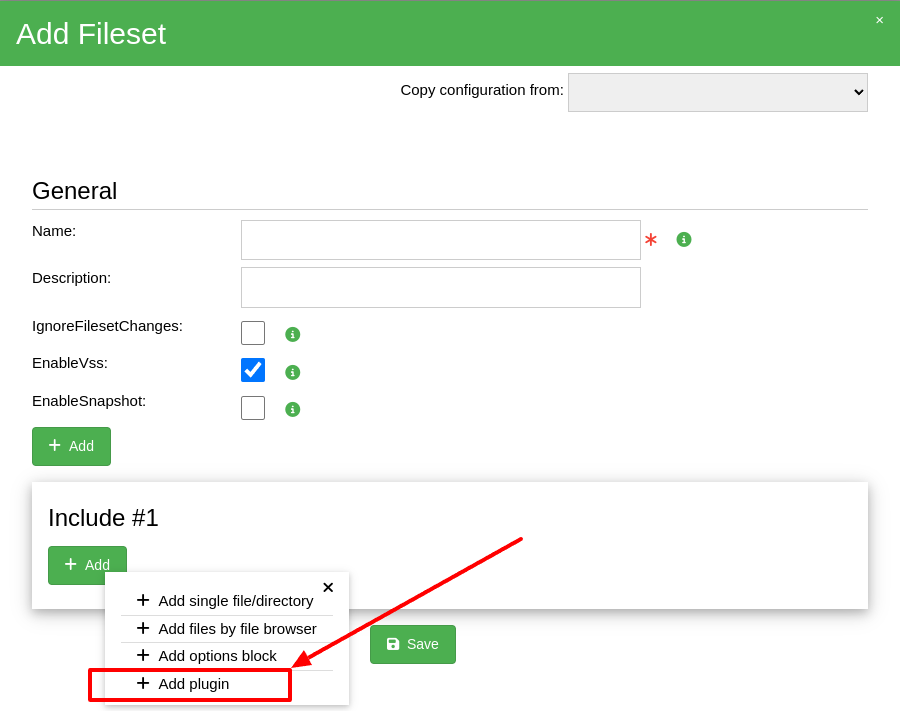
After clicking Add plugin, a configuration window opens (see below), allowing you
to configure and use the SQL Server plugin. Select the second or third option depending
on your needs.
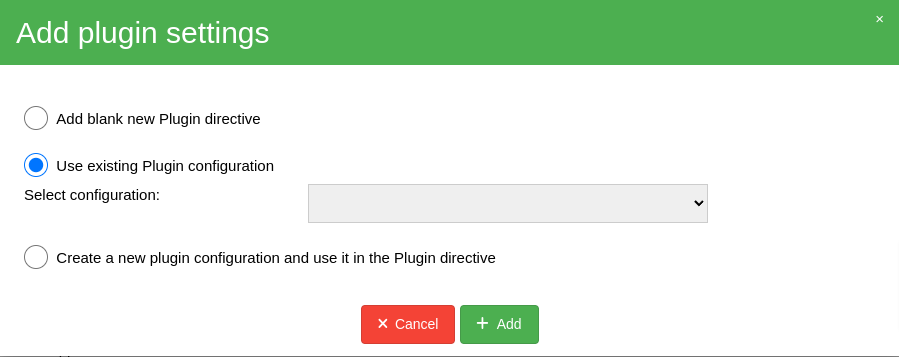
NOTE: After adding the Plugin directive, remember to save the FileSet resource.
Restore#
Restore to database server#
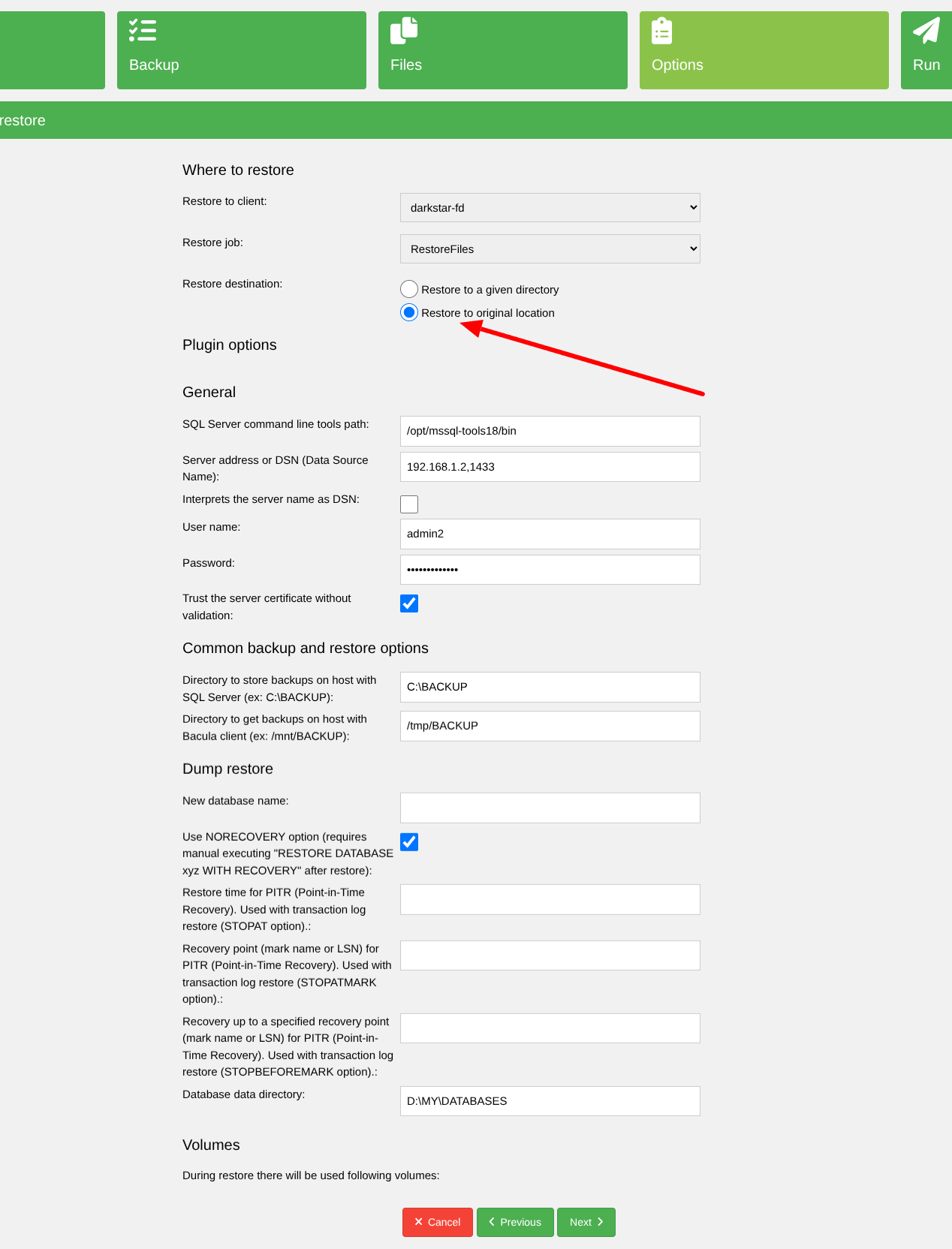
To restore backup data directly to the SQL Server instance, select Restore to original
location in the restore wizard. This option is supported for dump-based backups.
Restore to files#
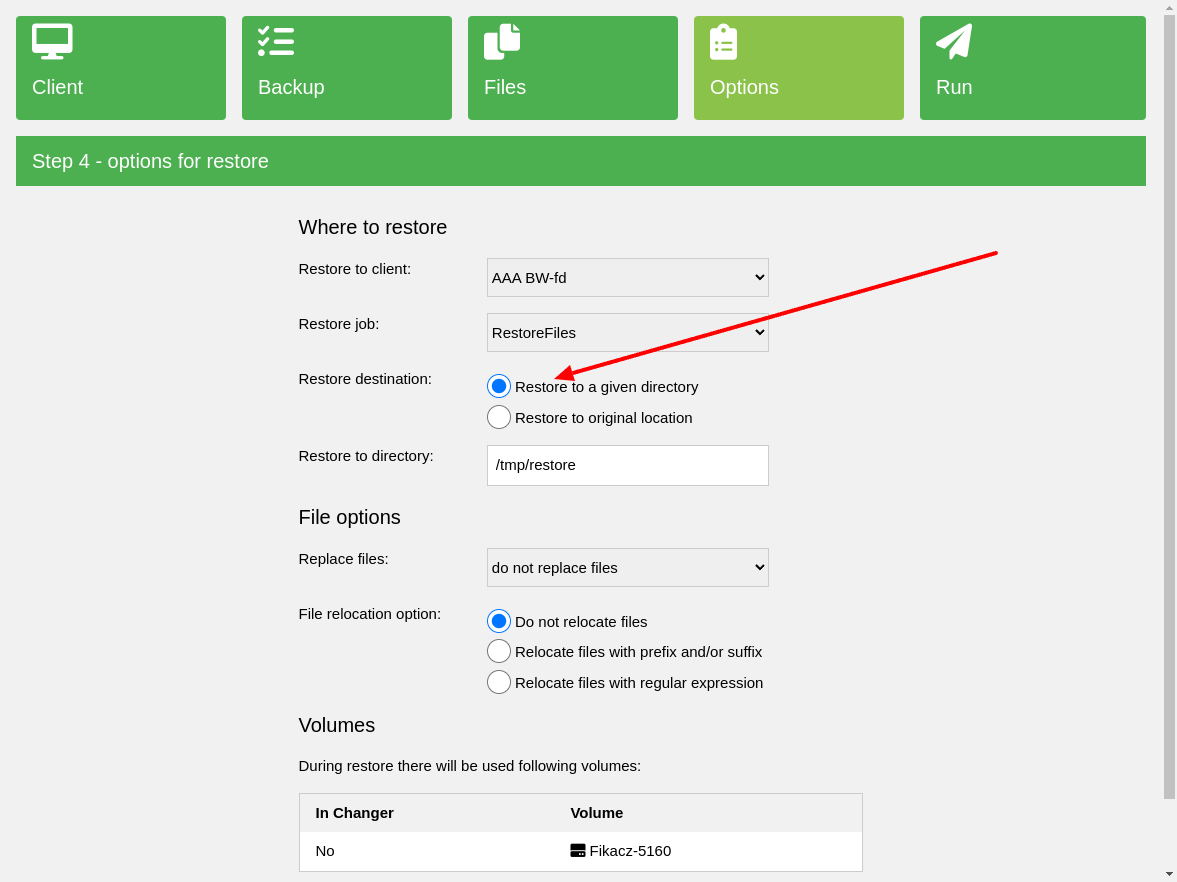
To restore backup data as files, select Restore to a given directory, which is the
default option.
Common configuration#
The plugin provides several general options common to all backup methods.
Common backup and restore parameters#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
SQL Server command line tools path |
|
This is directory path with Tools for Microsoft SQL Server binaries. |
No |
Server address or DSN (Data Source Name) |
|
This is the SQL Server address in form |
Yes |
Interprets the server address as DSN |
|
If used, then |
No |
Database server user name |
|
The username that should be able to log in and do backup and restore |
Yes |
Database server user password |
|
The database user password |
Yes |
Trust the server certificate without validation |
|
Useful if the certificate is not possible to successfully validate |
No |
User defined SQL Server name (any string) |
|
This name is used in the directory tree in the backed up data |
Yes |
Common backup directory to store backups on host with SQL Server |
|
This directory should be available and should be readable/writable by the user account running the SQL Server service. |
Yes |
Common backup directory to get backups on host with Bacula client |
|
This directory should be the same location as |
Yes |
Restore parameters#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
New database name |
|
This option is used to restore database with a new name. This option should be used only if restored is one database, not many. To restore many databases, this option should stay empty. |
No |
Use NORECOVERY option |
|
This option is recommended for every database restore to switch the database in |
No |
Restore time for PITR (Point-in-Time Recovery). |
|
Used to restore database to given point in time. Used with transaction log restore (STOPAT option). |
No |
Recovery point (mark name or LSN) for PITR (Point-in-Time Recovery). |
|
Used to restore database to given LSN (Log Sequence Number). Used with transaction log restore (STOPATMARK option) |
No |
Recovery point (mark name or LSN) for PITR (Point-in-Time Recovery). |
|
Used to restore database to a point before given LSN (Log Sequence Number). Used with transaction log restore (STOPBEFOREMARK option) |
No |
Database data directory |
|
Useful if you want to restore database files to SQL Server to given custom path or to different SQL Server instance |
No |
Dump backup method#
Levels#
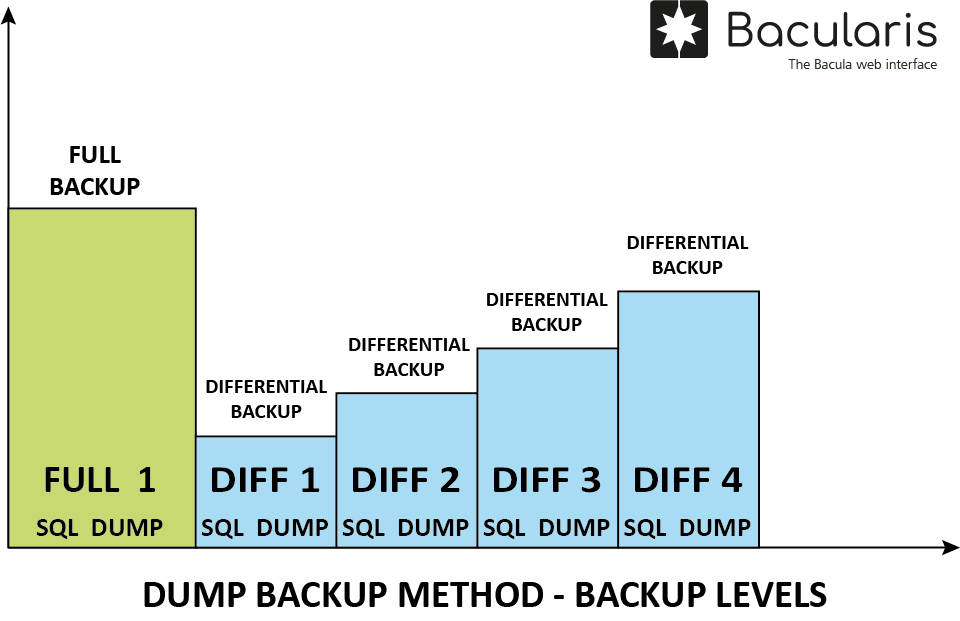
The following levels are supported in this SQL Server dump backup:
Full- backs up all data
Differential- backs up data changed since the last full backup
Requirements#
Ensure the Bacula client host has the following installed:
Bacularis version
5.9.0or higher
sqlcmd(part of Tools for Microsoft SQL Server)Bacula
bpipeplugin in the Bacula client
Prepare environment#
Before using the SQL Server dump backup method, verify that all environment requirements are met.
Dump all databases#
Description#
This backup type enumerates all databases on the server and backs them up one by one in SQL Server’s binary dump format.
Its main advantage is the ability to restore individual databases. Databases can be restored either directly to SQL Server (under their original or new names) or to local filesystem files.
Full backups also include the SQL Server system databases:
master
model
msdb
These may be useful when restoring an entire server or recovering from system database corruption.
Backup data structure#
Example directory structure for this backup type:
/
/#MSSQLDBBackup
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.SYSTEM
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.SYSTEM/master.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.SYSTEM/msdb.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.SYSTEM/model.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53830-2025-11-30_061440-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53832-2025-11-30_061515-Differential.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53830-2025-11-30_061440-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53832-2025-11-30_061515-Differential.bak
The file descriptions are the following:
.SYSTEM- contains system database backups.
master.bak- stores server-wide metadata, configuration, login data, and physical file locations
msdb.bak- stores backup history, restore history, SQL Agent jobs, schedules, alerts, etc.
model.bak- contains default database settings and initialization structures
sql-data-*-Full.bak- is created on full backup and contains the full binary database backup
sql-data-*-Differential.bak- is created on differential backup and contains the differential binary database backup
Configuration#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Enable dump backup method |
|
This is an option to enable dump backup method at all. Without this option enabled none of dump backup types works. |
Yes |
Backup all databases |
|
Enable dumping all databases, each in a separate dump |
Yes |
Delete local database backup copy at the end of backup |
|
The backups are stored in common backup directory before they are sent to Bacula client. With this options the local backup copy in common directory is deleted just after backup. |
No |
Use compression |
|
Use software compression for backup data |
No |
Copy-only backup |
|
The copy-only backup is independent of the sequence of conventional SQL Server backups. |
No |
Dump selected databases#
Description#
This backup type allows selecting specific databases to back up. It is useful when only
certain databases need protection. System databases (master, model, msdb)
are not included.
Restoration is possible both directly into SQL Server and as a file restore.
Backup data structure#
Below you can see example data structure for this dump backup type that can be restored to the database server or in form of the file restore.
/
/#MSSQLDBBackup
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53830-2025-11-30_061440-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53832-2025-11-30_061515-Differential.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53830-2025-11-30_061440-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53832-2025-11-30_061515-Differential.bak
The file descriptions are the following:
sql-data-*-Full.bak- is created on full backup and contains the full binary database backup
sql-data-*-Differential.bak- is created on differential backup and contains the differential binary database backup
Configuration#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Enable dump backup method |
|
This is an option to enable dump backup method at all. Without this option enabled none of dump backup types works. |
Yes |
Databases to backup (comma separated) |
|
Enable dumping selected databases, each in a separate dump |
Yes |
Delete local database backup copy at the end of backup |
|
The backups are stored in common backup directory before they are sent to Bacula client. With this options the local backup copy in common directory is deleted just after backup. |
No |
Use compression |
|
Use software compression for backup data |
No |
Copy-only backup |
|
The copy-only backup is independent of the sequence of conventional SQL Server backups. |
No |
Transaction log backup#
Description#
With this backup method are backed up the transaction logs (Write-Ahead Logs).
This method is useful if there is needed to have a transaction log backup for the Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR).
This backup method can be used together with the dump backup method and in many cases it is very good choice to have powerful database backup protection.
Levels#
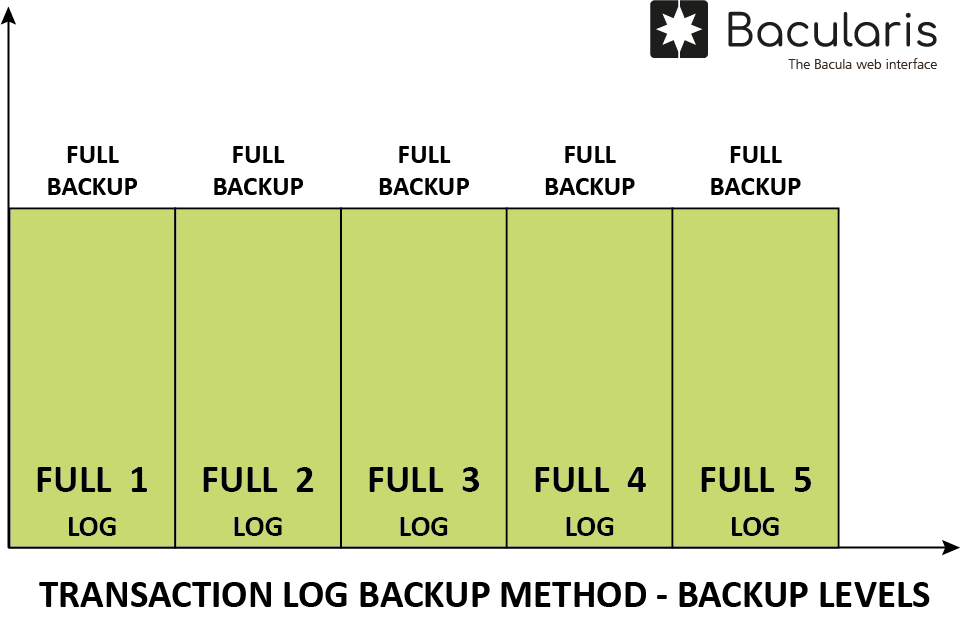
This backup method always does the full current transaction log backup
regardess of the current backup level. The transaction log is a different
chain from the dump backup levels (Full, Differential) and does not
start from the last dump backup.
The full log backup method is done with jobs running with level:
Full
Incremental
Differential
Backup data structure#
Below you can see example data structure for this transaction log backup method
that can be restored directly to the SQL Server database (together with
Full/Differential backups) or in form of the local file restore.
This list below shows the transaction log data used together with dump backup data:
/
/#MSSQLDBBackup
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53921-2025-11-30_134127-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/transaction-log-53921-2025-11-30_134127-Full.trn
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/sql-data-53922-2025-11-30_134151-Differential.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/transaction-log-53922-2025-11-30_134151-Differential.trn
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseA/transaction-log-53923-2025-11-30_134319-Incremental.trn
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53921-2025-11-30_134127-Full.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/transaction-log-53921-2025-11-30_134127-Full.trn
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/sql-data-53922-2025-11-30_134151-Differential.bak
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/transaction-log-53922-2025-11-30_134151-Differential.trn
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/databaseB/transaction-log-53923-2025-11-30_134319-Incremental.trn
The file descriptions are the following:
sql-data-*-Full.bak- is created on full backup and contains the full binary database backup
sql-data-*-Differential.bak- is created on differential backup and contains the differential binary database backup
transaction-log-*-Full.trn- is created on full backup and contains the transaction log backup
transaction-log-*-Differential.trn- is created on differential backup and contains the transaction log backup
transaction-log-*-Incremental.trn- is created on incremental backup and contains the transaction log backup
Configuration#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Enable transaction log backup method |
|
This is an option to enable transaction log backup method at all. Without this option enabled the transaction log backup will not work. |
Yes |
Backup transaction logs for all databases |
|
This backs up all database transaction logs |
No |
Backup selected database transaction logs (comma separated) |
|
This parameter provides selected database list to back up transaction logs |
No |
Delete local log backup copy at the end of backup |
|
The transaction log backups are stored in common backup directory before they are sent to Bacula client. With this options the local log backup copy in common directory is deleted just after backup. |
No |
Copy-only transaction log backup |
|
The copy-only log backup is independent of the sequence of conventional SQL Server log backups. |
No |
Encryption data backup#
Description#
This backup method is for backing up encryption data such as Service Master Key (SMK), Database Master Keys (DMK) and certificates with private keys (PFX format). All encryption data can be additionally encrypted with password for backup purpose.
Having the encryption data backup can be useful in various situations, for example:
if you use Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for your databases
if you want to restore encrypted database to a new location
if you change the system user account for SQL Server service
…others
Note
Encryption data is backed up from the SQL Server but to restore there always should be used restoring to files (local file restore) and next manually imported to the SQL Server. This plugin does not support restoring encryption data directly to the SQL Server.
Levels#
The encryption data is backed up on the Full backup level.
Backup data structure#
Below you can see how the encryption data structure looks in backup:
/
/#MSSQLDBBackup
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/database-cert-databaseA.crt
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/database-cert-databaseB.crt
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/database-master-key-databaseC.key
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/database-master-key-databaseD.key
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/database-master-key-dastabaseE.key
/#MSSQLDBBackup/SERVER_XYZ/main/.ENCRYPTION/service-master-key-master.key
The file descriptions are the following:
.ENCRYPTION- special directory for storing encryption data
database-cert-*.crt- certificate with private key
database-master-key-*.key- Database Master Key (DMK)
service-master-key-*.key- Service Master Key (SMK)
Configuration#
Name |
Parameter |
Description |
Required |
|---|---|---|---|
Enable encryption data backup method |
|
This is an option to enable encryption data method at all. Without this option enabled the encryption data backup will not work. |
Yes |
Backup Service Master Key (SMK) |
|
This backs up the Service Master Key (SMK) |
No |
Protect Service Master Key (SMK) backup by password |
|
This is password to encrypt the Service Master Key backup |
No |
Backup Database Master Keys (DMK) for all databases |
|
This backs up Database Master Keys for all databases. If database does not have the key created, it is skipped in backup. |
No |
Backup Database Master Keys (DMK) for selected databases (comma separated) |
|
The Database Master Keys backup for selected databases. If database does not have the key created, it is skipped in backup. |
No |
Protect Database Master Key (DMK) backups by password |
|
This is password to encrypt the Database Master Key backup |
No |
Backup database TDE certificates with keys |
|
Backup certificates with private keys in PFX format |
No |
Protect the certificate backup by password |
|
This is password to encrypt the certificate file content |
No |
